2.1 Loading data
The two most popular formats to store data are text files and Excel/OpenOffice files. Both formats can be loaded into RStudio with just a few mouse clicks. You only need to choose File/Import Dataset, and a graphical interface for data import will appear – see Figure 2.1.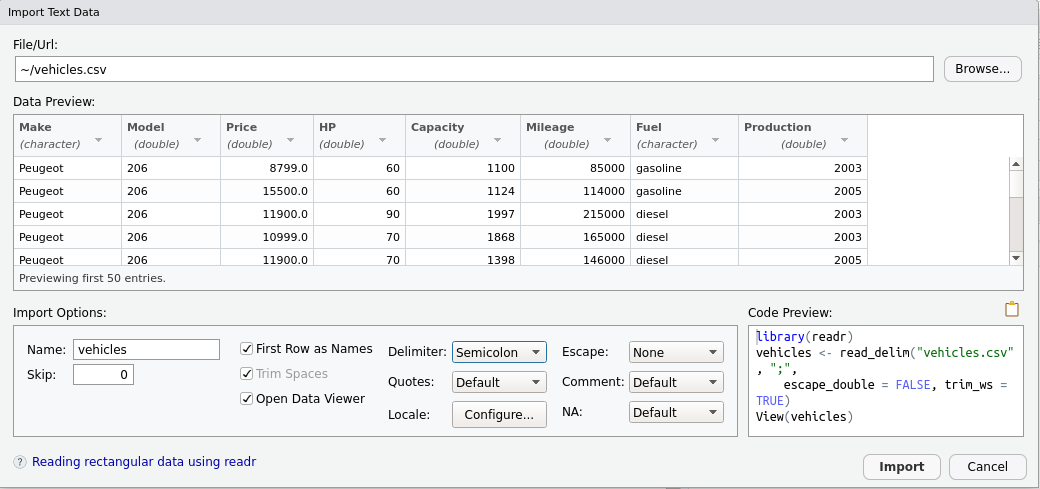
Figure 2.1: An example of the RStudio program window for importing data using a graphical interface.
If we encounter an untypical file formatting, we can use a few control buttons to specify what the separator is, whether the first row contains headers etc.
If we do not use RStudio, we can use function read.table() to load data. An example of this function is given below.
File http://www.biecek.pl/R/auta.csv contains data on 2400 sales offers for cars of different makes. This data is stored in a file with .csv extension. Each offer contains 8 parameters which are separated with semicolons in the text file.
A fragment of the file is shown below.
"Make";"Model";"Price";"HP";"Capacity";"Mileage";"Fuel";"
Production"
"Peugeot";"206";8799;60;1100;85000;"gasoline";2003
"Peugeot";"206";15500;60;1124;114000;"gasoline";2005
"Peugeot";"206";11900;90;1997;215000;"diesel";2003
"Peugeot";"206";10999;70;1868;165000;"diesel";2003
"Peugeot";"206";11900;70;1398;146000;"diesel";2005
"Peugeot";"206";19900;70;1398;86400;"diesel";2006
...The first argument of read.table() is the path to the file with the data. The file can be located on a hard drive, or on the Internet.
The next two arguments in the function execution below specify that the values in subsequent columns are separated with semicolons, and that the first row contains variable names.
The result of function read.table() – the table with data – is assigned to the vehicles symbol using the <- operator.
vehicles <- read.table("vehicles.csv",
sep = ";", header = TRUE)
head(vehicles)## Make Model Price HP Capacity Mileage Fuel Production
## 1 Peugeot 206 8799 60 1100 85000 gasoline 2003
## 2 Peugeot 206 15500 60 1124 114000 gasoline 2005
## 3 Peugeot 206 11900 90 1997 215000 diesel 2003
## 4 Peugeot 206 10999 70 1868 165000 diesel 2003
## 5 Peugeot 206 11900 70 1398 146000 diesel 2005
## 6 Peugeot 206 19900 70 1398 86400 diesel 2006The head() function shows the first 6 rows from the data set. This function allows us to quickly find out what the table contains.
In Section 2.6 we discuss more methods of data loading using various formats.
Once we have our data in place, it is time to work with it.